GGR plays a crucial role in maintaining the financial health of the iGaming industry. From casino games to sports betting. Gross gaming revenue is a key metric that provides essential insights into the financial performance of this sector.
Gross Gaming Revenue (GGR) provides a clear picture of the industry’s overall size and performance. As an example, in 2023, the U.S. gambling industry achieved a GGR of $66.65 billion, a $6 billion increase from the previous year. The largest portion of this revenue came from casino slots and table games.
What is Gross Gaming Revenue?
Gross Gaming Revenue (GGR) is the total amount of money a game operator earns from various gaming activities without deducting taxes and other expenses. GGR is the difference between the total amount a player places a bet on and the amount he gets after winning.
By monitoring the GGR, a game operator or brand can make effective decisions to improve their business offerings and services. As a result, they can further grow their iGaming business.
Formula for Gross Gaming Revenue
Understanding how to calculate GGR is essential for any gambling operator, whether new or experienced. Different operators may have their own methods or specific items included in their calculations. This calculation helps operators assess performance and manage business growth effectively.
Here’s the Formula for Gross Gaming Revenue Calculation:

Key Elements for GGR
Total Bet – Refers to the sum of all bets placed by all players
Total Winning – Refers to the total amount of money the operator gives back to players as their winnings.
Let’s understand how to calculate the GGR.
Let’s say you visit a gaming parlor and place a bet on poker of $50,000. After playing, you win $30,000 back. The gaming parlor’s GGR would be the difference between the amount you bet and the winnings.
GGR = $50,000 (total bets) – $30,000 (winnings) = $20,000
So, the gaming parlor would keep $20,000 as its GGR from your bet. This amount doesn’t include any expenses the parlor may have, like staff salaries or taxes—it’s just the money they made from the bets you placed.
Gross Gaming Revenue on a Financial Statement
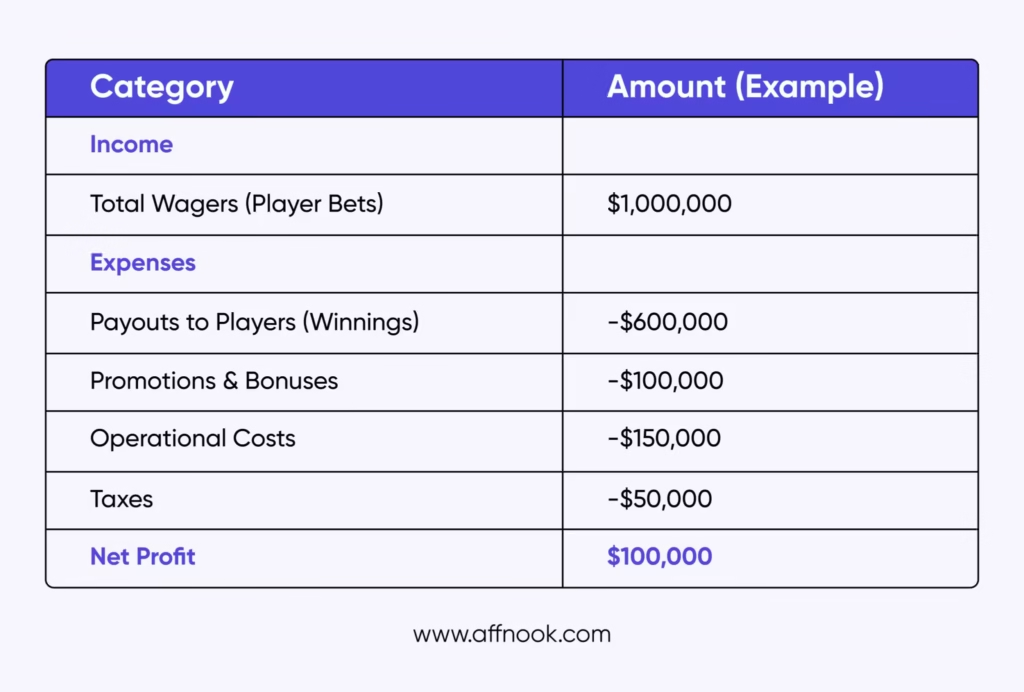
Net profit is just one component of GGR. While the calculation of GGR can vary between operators, it generally includes a range of income and expense categories.
For example, the total wagers (player bets) contribute to the GGR, while payouts to players, promotions and bonuses, operational costs, and taxes are deducted as expenses. Each operator or brand may have its own method of breaking down GGR, factoring in specific business expenses.
Adjusted Gross Gaming Revenue (AGGR)
With the help of GGR, you can measure how much money is generated from gaming activities. However, the GGR does not always give you an idea of the total profit you are making. It does not account for other expenses like bonuses, marketing expenses, and so on. To resolve this problem in the calculation, you can go for the Adjusted Gross Gaming Revenue (AGGR) instead.
Adjusted Gross Gaming Revenue is an enhanced metric, which helps to subtract the other operational expenses (promotional, taxes, or any other payouts) from GGR to showcase the proper insight of operator net revenue. It plays a very important role in refining the actual income of the operator, which helps to retain and maintain the players.
Let’s understand the concept with an example.
For example, let’s assume a casino earns $500,000 in GGR, but spends $100,000 on player bonuses and $50,000 on promotions. To calculate AGGR, you subtract these expenses from the GGR:
AGGR = $500,000 – $100,000 (bonuses) – $50,000 (promotions) = $350,000.
So, after accounting for these costs, the adjusted revenue is $350,000.
Factors Affecting Gross Gaming Revenue
A proper understanding of each factor will help you increase your business revenue. It can additionally assist you in finding loopholes where you can level up performance, like boosting cash flow and reducing attrition rate. Here are five key factors that influence GGR, and tips on how to maximize your gaming revenue.
Game Selection and House Edge
To attract players, it is important to offer a wide range of games. But this can be quite costly. Before signing any deal with a software provider, review the revenue share they are asking for. Using a game aggregator might be a smarter choice if you want to conserve your budget.
The house edge you set also has a big impact on your GGR. If you are getting a higher profit margin, it means you can make more money in a short period. But you can lose your players in the long run. Striking the right balance between house edge and player satisfaction is key to sustaining long-term GGR growth.
Consumer Behaviour and Preferences
Being able to meet players’ needs will impact your gross gaming revenue. You can go about this in many different ways. But the best method is to cater to as many players as possible. You can do that by regularly analyzing what users want and tailoring your offer to suit their preferences.
By enhancing your SEO strategies, you can increase your online presence, which helps players find your platform easily. This approach not only helps you to get more players but also allows you to create unique gaming experiences that magnify your GGR through loyalty.
Competition and Market Dynamics
Entering crowded markets or segments requires a highly competitive offer to grab attention and stand out. Create a strategic roadmap to achieve your goals. Planning and executing tactical moves will help you not only cement a spot in the market but also stay one step ahead.
Use digital marketing strategies to build a strong online presence that attracts and engages more players. As an outcome, you can grow your revenue and keep meeting business goals.
Financial and Regulatory Ecosystem
Changes in the economy and regulations in your area of operation can affect your gross gaming revenue. Even highly reputed or widely used platforms are not exempt from being affected by these factors. On the other hand, even mismanaged iGaming businesses can earn a profit if the economic conditions are favorable.
Understanding this ecosystem can help operators face challenges and optimize their revenue streams so that they can earn and maintain their profits despite fluctuations in market conditions.
Why does GGR matter?

GGR vs. NGR: What’s the Difference?
In iGaming, two important revenue metrics often get mixed up: Gross Gaming Revenue (GGR) and Net Gaming Revenue (NGR).
- Gross Gaming Revenue (GGR): This is the total amount wagered by players minus their winnings. It shows the “top-line” earnings before any costs.
- Net Gaming Revenue (NGR): This is what operators actually keep after subtracting bonuses, taxes, affiliate commissions, and other expenses.
Example: If a casino earns $1,000,000 in GGR but spends $200,000 on bonuses, $100,000 on taxes, and $50,000 on affiliate commissions, the NGR would be $650,000.
For affiliates and operators, understanding NGR is crucial since it reflects true profitability and is often the base for revenue-sharing agreements.
Summing Up
A deep understanding of gross gaming revenue is vital for everyone who is involved in the iGaming industry, from operators to investors. These metrics help maintain the financial stability of gaming operations and provide a comprehensive view of the industry’s economic impact.
Calculating the GGR can provide any iGaming entity with valuable insights about their business. As a result, you can make effective decisions and plans. Whether you’re a player, operator, or investor, understanding GGR is essential for navigating the dynamic world of gaming.
Help Section
What is Gross Gaming Revenue in iGaming?
Gross Gaming Revenue (GGR) is the total amount of money wagered by players minus their winnings over a specific period. It represents the top-line revenue before deductions like bonuses, taxes, or operational costs. GGR is a critical metric for operators to measure the popularity and profitability of games.
How is Gross Gaming Revenue calculated for online casinos?
The formula for GGR is:
GGR = Total Bets – Player Winnings
For example, if players wager $1,000,000 and win $700,000, the GGR is $300,000. This metric helps operators understand game performance, player behavior, and market demand before accounting for expenses.
Why is Gross Gaming Revenue important for iGaming operators and affiliates?
GGR is a foundational metric for decision-making because it:
Informs strategy: Operators use GGR to optimize marketing spend, product selection, and bonus structures.
Measures market performance: Shows which games and products generate the most revenue.
Drives affiliate commissions: Many programs base payouts on a percentage of GGR.
What is the difference between Gross Gaming Revenue (GGR) and Net Gaming Revenue (NGR)?
GGR: Top-line revenue = Total bets – winnings.
NGR: Actual revenue after deducting bonuses, taxes, and fees.
GGR shows how much money enters the system, while NGR reflects profitability and sustainable revenue, making both metrics critical for iGaming operators and affiliates.
How can iGaming operators increase Gross Gaming Revenue in regulated markets?
Operators can boost GGR by:
- Offering popular and engaging games like slots, live casino, and esports betting.
- Designing attractive promotional campaigns that drive wagers without excessive bonus leakage.
- Leveraging data analytics to optimize game placement, user experience, and retention.
- Expanding into multiple regulated markets while adhering to compliance standards.
By focusing on game engagement and responsible promotions, operators can grow GGR while maintaining regulatory compliance.




